CSS Animation – Digital Animation
What is digital animation. Who invented computers, how did it influence animation. Let’s travel through time and find out in this article.
Introduction
Computers and digital animation are inseparable. Our imagination and creativity push both, producing wondrous stories, mind-boggling worlds and fantastic beasts.
In this article, we’ll learn the history of computer animation. When computers transformed from analog to digital, learn the basics of Two-dimensional (2D) and Three-dimensional (3D) computer animation.
History of Computer Animation
Digital computers are ubiquitous. We have them in our pockets, on our workstations and on our bodies. Smartphones, tablets, smartwatches, laptop and desktop PCs are indispensables items. We use them daily to be both productive and entertained.
The digital computer has come a long way.
Let’s go back in time, explore how the digital computer was invented and how it revolutionized animation.
- Charles Babbage, English polymath, is credited for the concept of a digital programmable computer. His invention, the Analytical Engine, paved the way for more complex electronic designs found in modern computers.
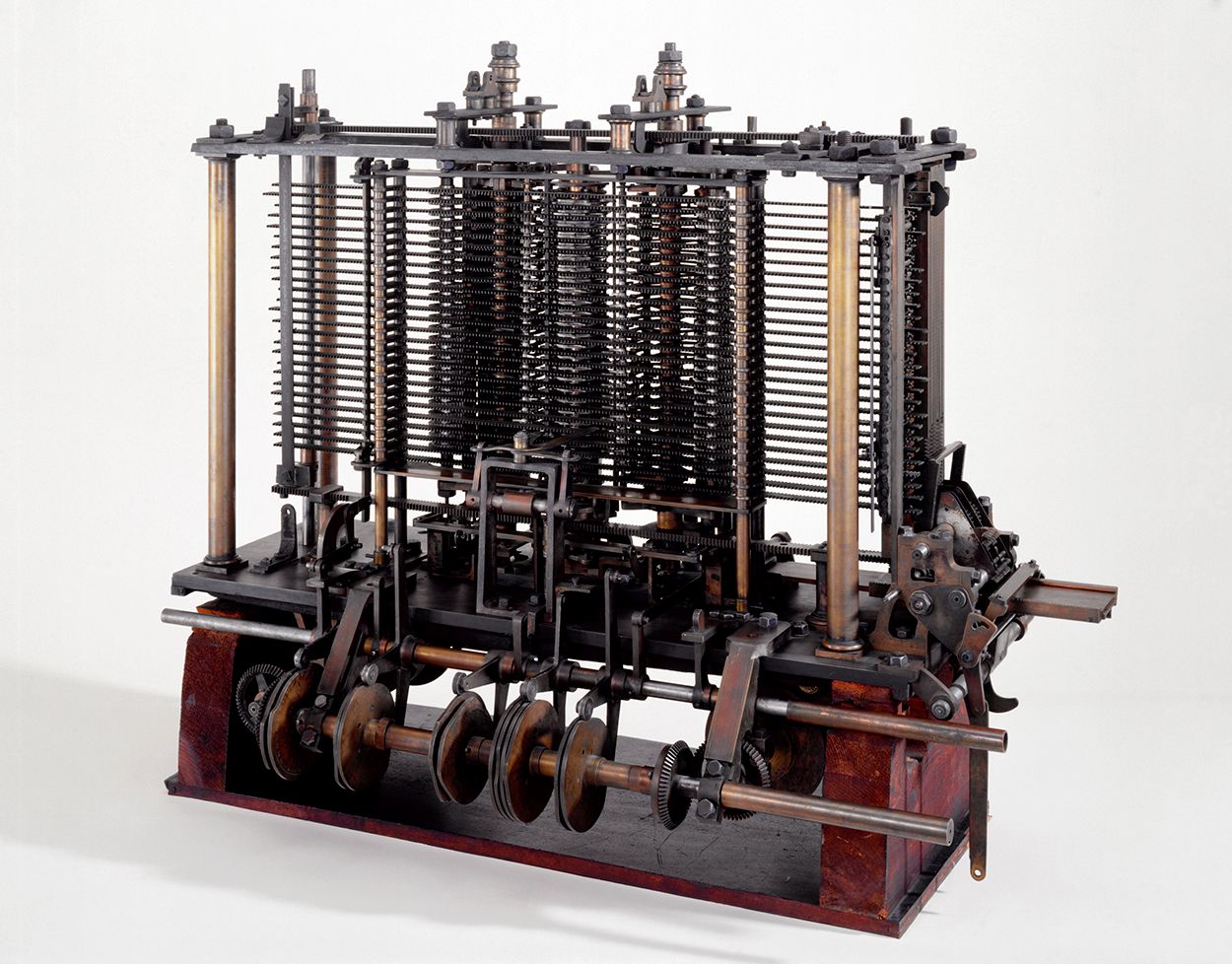
- George Boole, English mathematician, in 1854 formalized Boolean algebra, which became the basis of digital logic and computer science.
- Ada Lovelace, English mathematician, is credited to be the first computer programmer, publishing the first algorithm for use in Babbage’s Analytical Engine.
- Akira Nakashima, Japanese electrical engineer at NEC, from 1934 to 1936 introduced switching circuit theory, laying the foundations for digital circuit design used in digital computers.
- Alan Turing, English mathematician and cryptanalyst, in 1936 invented the Turing machine, widely considered to be the father of artificial intelligence and theoretical computer science.
- John Whitney, American animator, composer and inventor, considered to be one of the fathers of computer animation. Together with graphic designer Saul Bass, Whitney animated the title sequence, swirling graphics, for Alfred Hitchcock’s 1958 film Vertigo.
Futureworld (1976), a sequel to Michael Crichton’s Westworld, was the first major film to use 3D computer-generated imagery (CGI).

Snippets from two experimental short films, Edwin Catmull’s A Computer Animated Hand and Fred Parke’s Faces & Body Parts, were used for an animated hand and face sequence in the movie.
2D digital compositing was used in the movie to material characters over a background.
In the following sections, let’s look at Two-dimensional (2D) and Three-dimensional (3D) animation techniques.

2D Animation
Two-dimensional (2D) animation is a type of animation that animates objects with two parameters, a width and a height. All objects and characters in the animation remain within the x-axis and y-axis.
Digital 2D animation is considered an evolution from traditional, hand-drawn animation known from the 1800s.
The most significant difference between traditional, hand-drawn animation and modern 2D animation process is 2D animation software have built-in tweening features.
Tweening is short for inbetweening.
In hand-drawn animation, you have keyframes. These are the images at the beginning and end of a smooth transition.
Inbetweens are images between two key frames. Without inbetween images, animation will jerk, breaking the illusion of smooth motion.
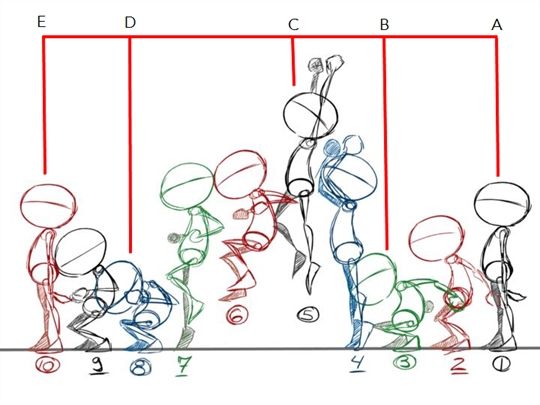
Primary artists drew the keyframes, then passed down to assistants to add necessary inbetween images, completing the animation.
Here’s a great digital keyframe and tweening demo.
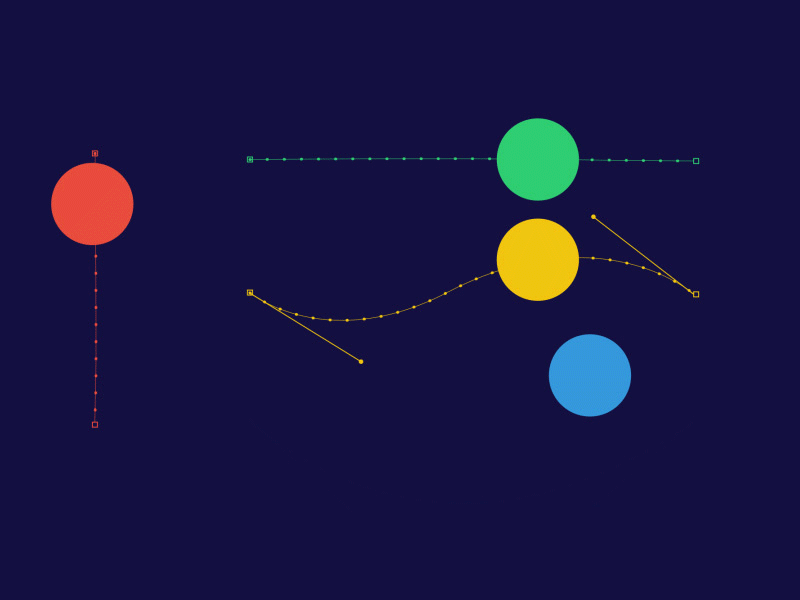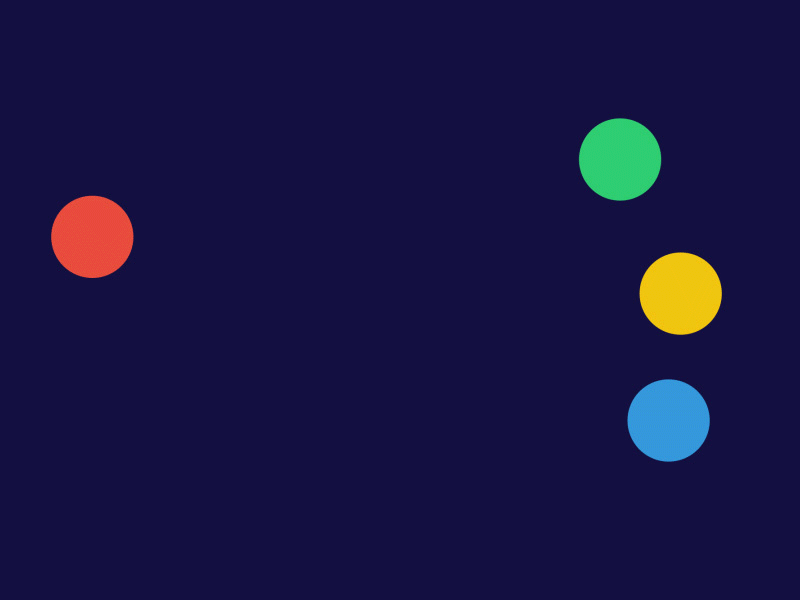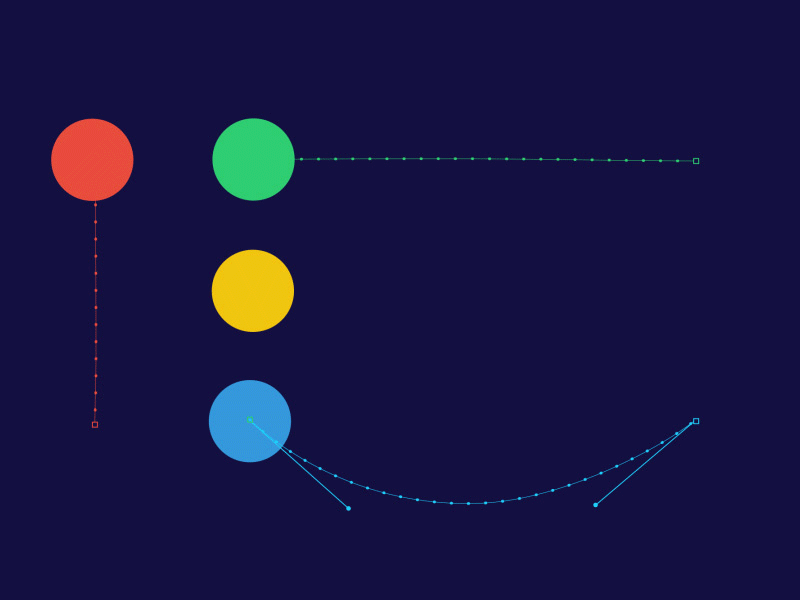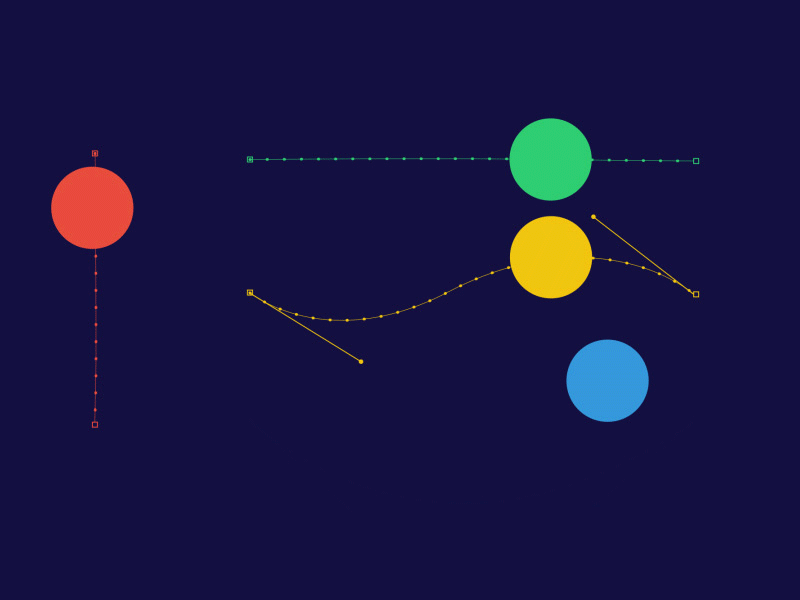
- Each ball has a beginning and end keyframe.
- Tweens are controlled with paths, producing animation between beginning and end keyframe.
- You can make acceleration and deceleration motion by adjusting the tween frames.
2D software commonly used by professional animators:
Now we know the basics of 2D animation, let’s explore 3D animation in the next section.
3D Animation
3D or Three-dimensional animation is a process that takes digital objects to create an illusion of life-like movement in a three-dimensional space.
Currently, flat or two-dimensional screens are used to display 3D animation. Through myriad production processes, these computer-generated objects appear to simulate movement in a 3D universe.
3D animation occurs on three axes:
- x-axis
- y-axis
- z-axis
Z-axis gives 3D animation its depth element.
While 2D animation is akin to drawing, 3D animation is more akin to sculpting.
3D animation characters are built from the inside out.
A typical 3D animation production follows these workflows:
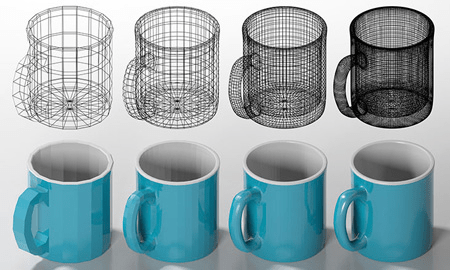
- 3D modeling – the process of creating an object or character’s 3D representation. 3D modeling artists, sometimes referred to as 3D modelers, use design data that may consist of sketches, drawings, sometimes sculptures or a combination of all three. Using 3D software packages, they recreate a 3D representation of the design data.
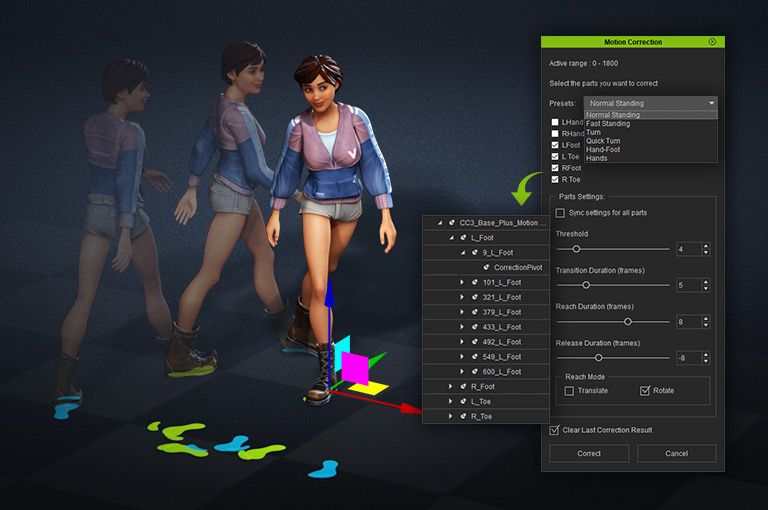
- Layout and animation – placement and movement of 3D objects within a scene. Lighting are placed to create a specific mood or artistic taste.
- 3D rendering – the process of generating or rasterizing an image based on the 3D model, lighting, and camera angles. Details such as light and shadows, reflections, transparency will be adjusted at this step.
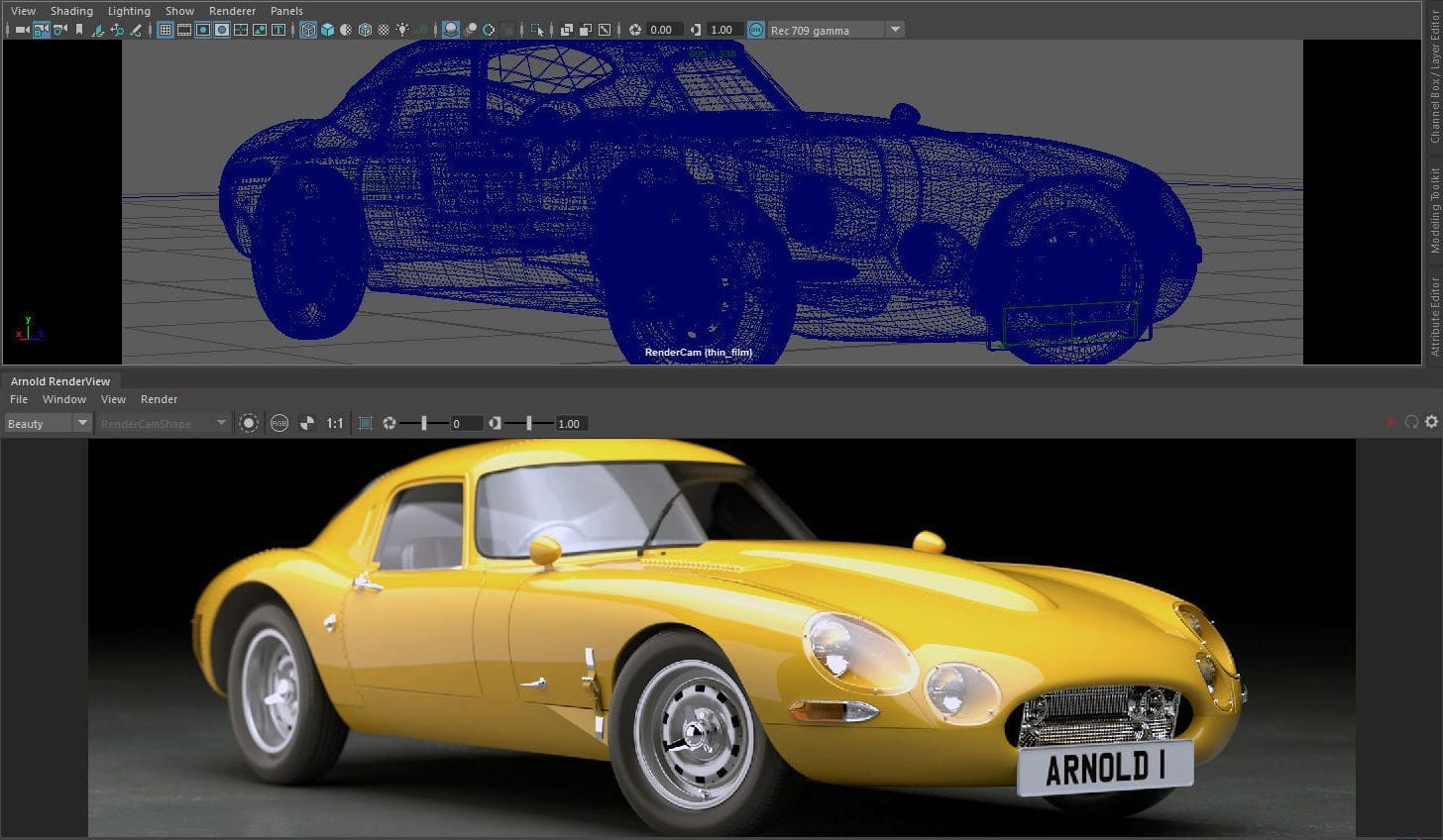
3D introduces depth in the characters and objects. Depth influences the placement of shadows and lighting, making it more complicated than 2D animation. But thanks to modern software and faster computers, 3D animators have an array of approaches and tools to create dazzling 3D animations faster.
3D software commonly used by professional animators:
Conclusion
Digital computers and digital animation has evolved hand in hand, pushing each other to their limits.
2D and 3D animation are becoming more sophisticated. Each new feature animation works on the previous blockbuster animation’s foundations. Animation software is improved at an ultra-high pace to meet demand from creative animators and story tellers.
How would computer pioneers Charles Baggage and Ada Lovelace react to present day animation and computer graphics? Would they describe it as “magic”?
Any sufficiently advanced technology is indistinguishable from magic. — Arthur C. Clarke
What animation do you deem magical? Share it with us on Twitter @pyxofy, on LinkedIn, Mastodon or Facebook.
We hope you liked this article. Kindly share it with your network. We really appreciate it.
Related Articles